Crater on Synology
Install Crater on Synology NAS. This is a program to track expenses and payments and create invoices.

Table of Contents
CAUTION
Please note that this blog post was originally written in German and has been translated for your convenience. Although every effort has been made to ensure accuracy, there may be translation errors. I apologize for any discrepancies or misunderstandings that may result from the translation and I am grateful for any corrections in the comments or via mail.
Crater
Crater is an open-source invoicing program.
Requirements
I use a Synology NAS. It is a DS220+(Amazon Affiliate Link) with 10 GB RAM(Amazon Affiliate Link).
However, Crater only requires a few resources. The instructions can also be applied analogously to other devices with Docker.
A reverse proxy manager in the network is helpful, regardless of whether it is located onanother device or the Synology NAS. Also, a domain accordingly.
Preparation
Docker should be installed on the NAS. I have written here more about setting up a Synology DiskStation.
User Docker
I first set up a Docker group for better rights management.
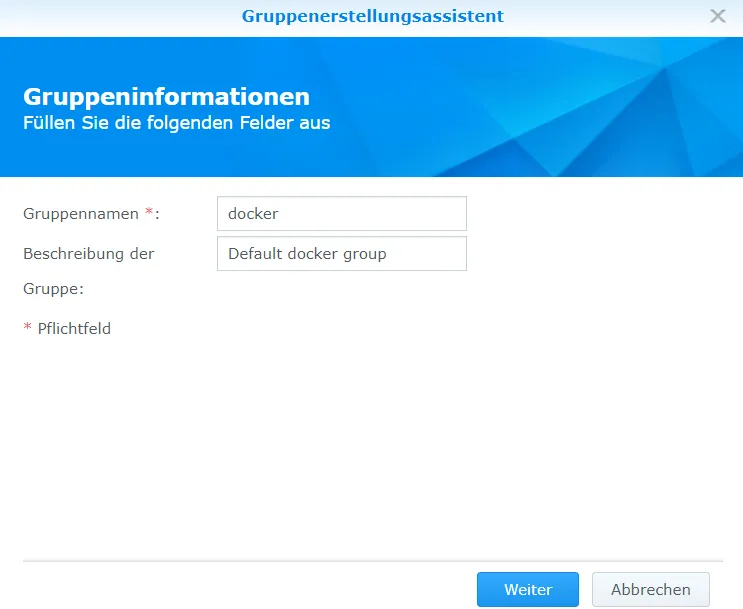
I create a new user who will ultimately have the rights to the Crater container.
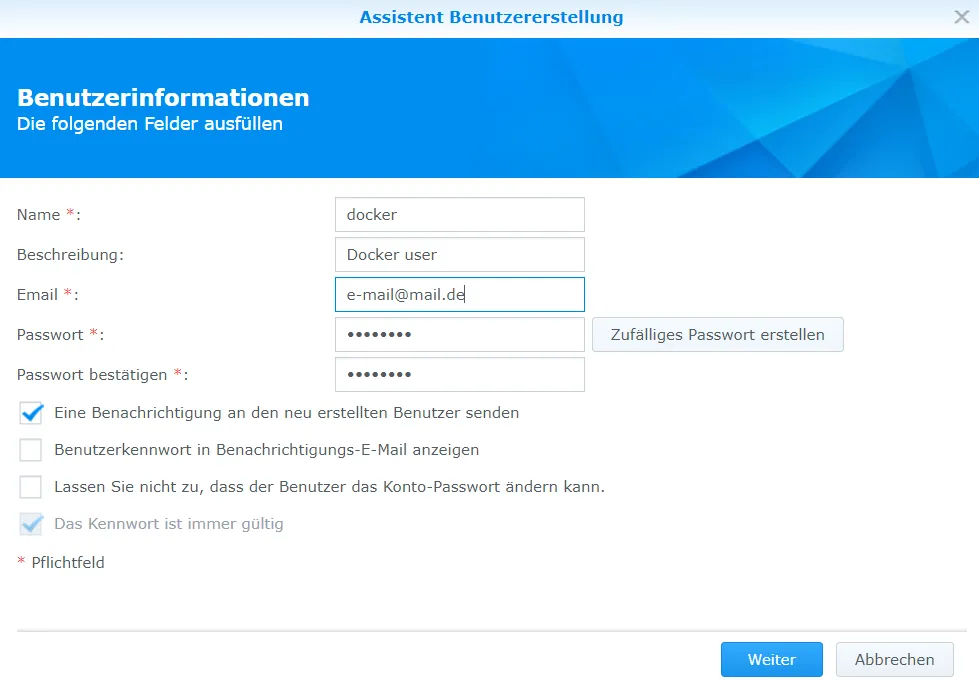
I add this user to the Docker group.
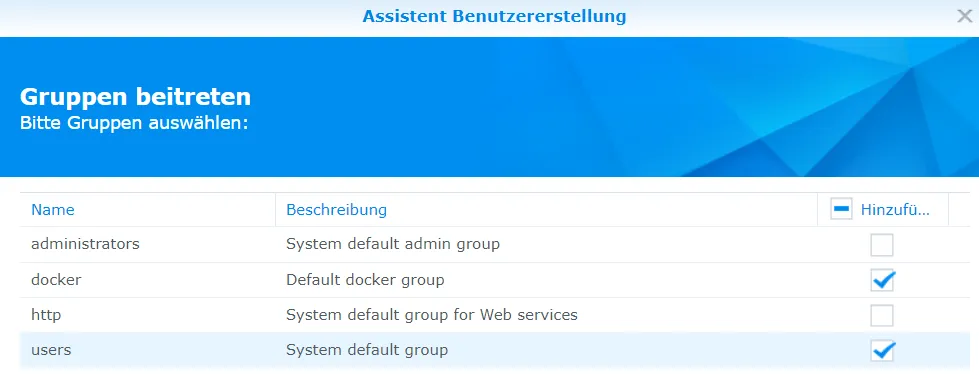
Creating a single user for each service is too time-consuming, so I only have one Docker user.
Crater folder
Next, I need a folder in which I want to save all the files. In my case, the folder ends up in the docker shared folder. I remember the path of the folder; in my case, it is /volume1/docker/crater, and I grant all permissions to the docker user.
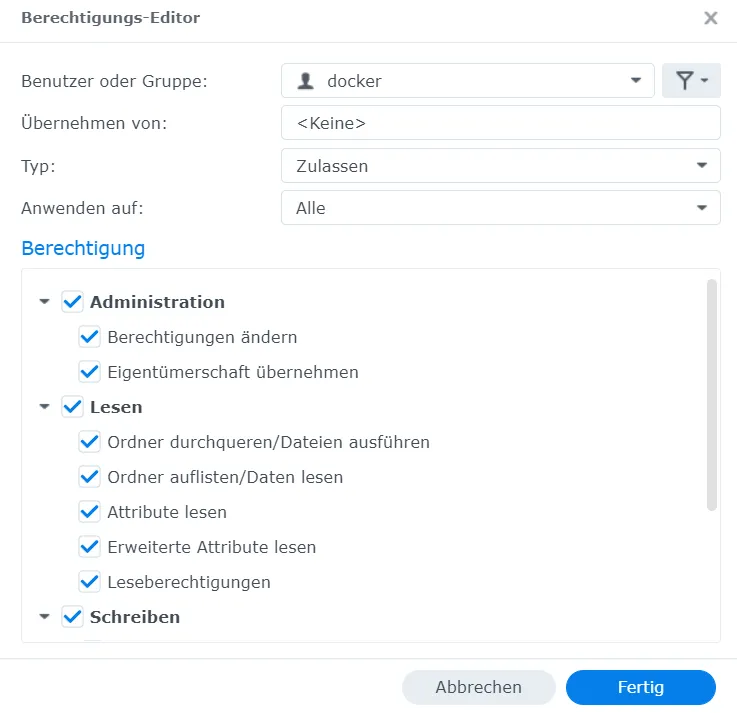
I also check the box that it should apply to subfolders.
Git Server
I install the Git server from the package center.
This makes it easier for me to clone the repository.
Crater Download
Next, I want to download Crater. To do this, I check the release page to see which version is the latest. Right now, it is version 6.0.6.
Next, I activate the SSH service and connect to the NAS via SSH.
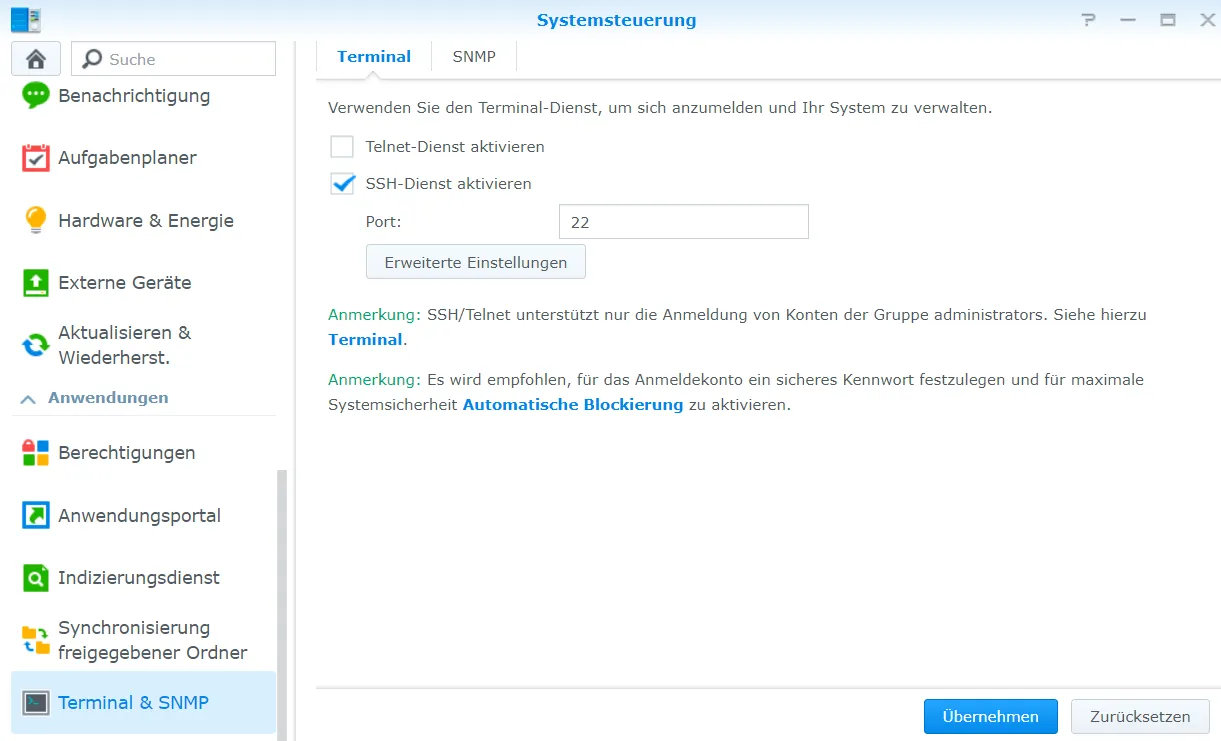
ssh adminusername@{ip-address-from-nas}I move to the Crater folder.
cd /volume1/docker/craterThen, I clone the repository.
git clone -b 6.0.6 https://github.com/crater-invoice/crater --single-branch .All the necessary files should now be in my folder.
I would like to know the UserID of the docker user.
id -u dockerI remember this number as the UserID.
Crater installation
Next, I copy the environment file.
cp .env.example .envAnd then I edit it:
vim .envAbout Vim: This is a text editor that is pre-installed by default. If you press i, you switch to edit mode. Press esc to exit edit mode again. If you are not in edit mode, you can exit the editor again with :q if you have not changed anything. If you have changed something, you can either save with :x or exit with :q! without saving.
Crater environment variables
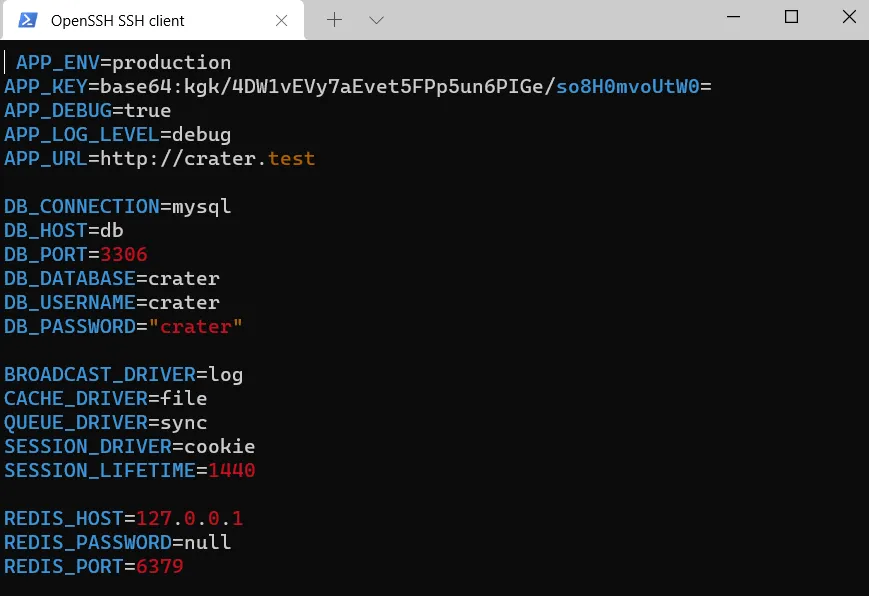
- I change APP_DEBUG to false
- I change APP_LOG_LEVEL to info
- APP_URL I change to my
https://crater.mydomain.de - DB_CONNECTION I change to pgsql
- DB_PORT I change to 5432
- DB_PASSWORD I change to my password
- Mail arguments are optional
- For SANCTUM_STATEFUL_DOMAINS and SESSION_DOMAIN I enter my domain (without
https://).
If you use localhost or the IP address, it looks something like this:
SANCTUM_STATEFUL_DOMAINS=localhost:8080
SESSION_DOMAIN=localhostI leave the rest and exit the file with :x.
Database folder
I create two new folders.
mkdir docker-compose/db
mkdir docker-compose/db-backupAdd Postgresql
Then I edit the Dockerfile and change two sections.
vim Dockerfile[...]
# Install system dependencies
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
git \
curl \
libpng-dev \
libonig-dev \
libxml2-dev \
zip \
unzip \
libzip-dev \
libmagickwand-dev \
mariadb-client \
libpq-dev
[...]
# Install PHP extensions
RUN docker-php-ext-install pdo_mysql mbstring zip exif pcntl bcmath gd pdo_pgsql
[...]Crater Docker Compose
The next step is to edit the docker-compose.yml.
vim docker-compose.ymlversion: "3"
networks:
internal:
external: false
services:
app:
container_name: crater-app
build:
args:
user: docker
uid: 1234
context: ./
dockerfile: Dockerfile
image: crater-app
restart: unless-stopped
working_dir: /var/www/
volumes:
- ./:/var/www
- ./docker-compose/php/uploads.ini:/usr/local/etc/php/conf.d/uploads.ini:rw,delegated
networks:
- internal
db:
container_name: crater-db
image: postgres:14
restart: always
volumes:
- ./docker-compose/db:/var/lib/postgresql/data:rw,delegated
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: crater
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: qwertzSMO4Yaqx7tUHhX
POSTGRES_DB: crater
networks:
- internal
db-backup:
container_name: crater-db-backup
image: postgres:14
volumes:
- ./docker-compose/db-backup:/dump
- /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
environment:
PGHOST: db
PGDATABASE: crater
PGUSER: crater
PGPASSWORD: qwertzSMO4Yaqx7tUHhX
BACKUP_NUM_KEEP: 10
BACKUP_FREQUENCY: 7d
entrypoint: |
bash -c 'bash -s <<EOF
trap "break;exit" SIGHUP SIGINT SIGTERM
sleep 2m
while /bin/true; do
pg_dump -Fc > /dump/dump_\`date +%d-%m-%Y"_"%H_%M_%S\`.psql
(ls -t /dump/dump*.psql|head -n $$BACKUP_NUM_KEEP;ls /dump/dump*.psql)|sort|uniq -u|xargs rm -- {}
sleep $$BACKUP_FREQUENCY
done
EOF'
networks:
- internal
redis:
container_name: crater-redis
image: redis
restart: unless-stopped
networks:
- internal
nginx:
image: nginx:1.17-alpine
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- 8011:80
volumes:
- ./:/var/www
- ./docker-compose/nginx:/etc/nginx/conf.d/
networks:
- internal
cron:
build:
context: ./
dockerfile: ./docker-compose/cron.dockerfile
volumes:
- ./:/var/www
networks:
- internalThe UID and the password for the database can be customized. The port can also be changed from 8011 to something else. Suppose the Proxy Manager is on the Synology. You can delete it in that case, provided you add nginx to the Proxy Manager network.
Then run sudo docker-compose up -d and wait.
Install Composer
Finally, the start script must be executed.
sudo ./docker-compose/setup.sh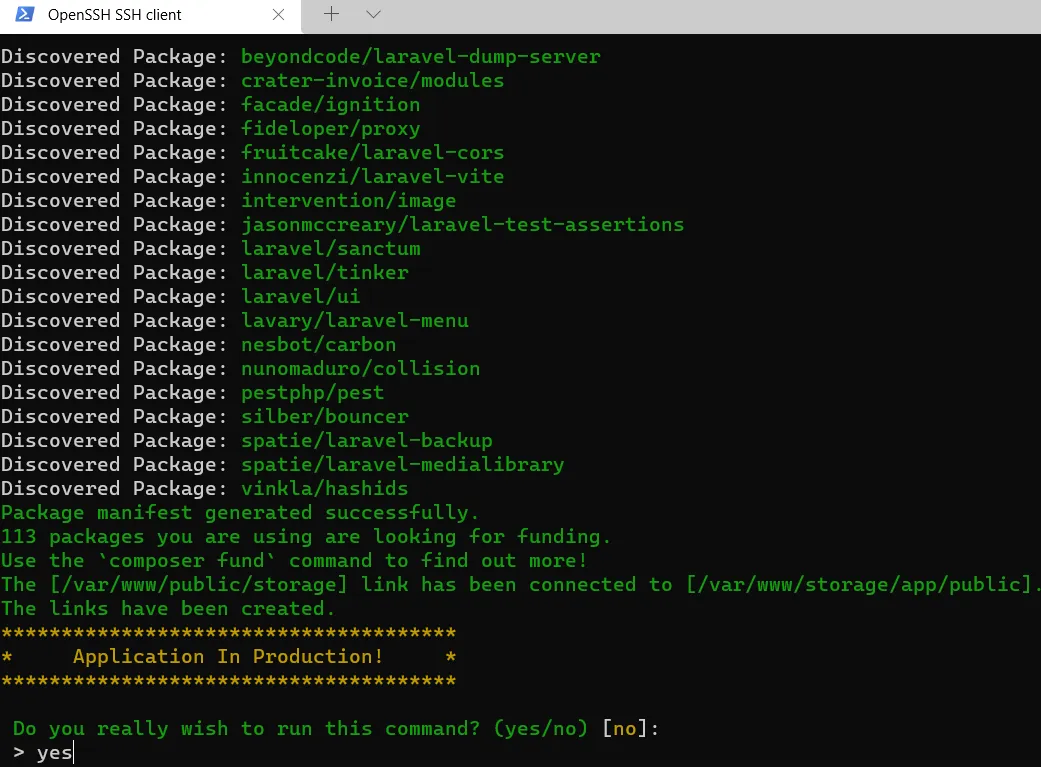
I then exit the terminal.
exitI also switch SSH off again.
![]()
Crater WebGUI
Now, I either call the IP address from the NAS with port 8011 or set up a proxy host.
I adjust a few of the values.
The database is pgsql, port 5432 and host db. The rest should be self-explanatory.
Backup
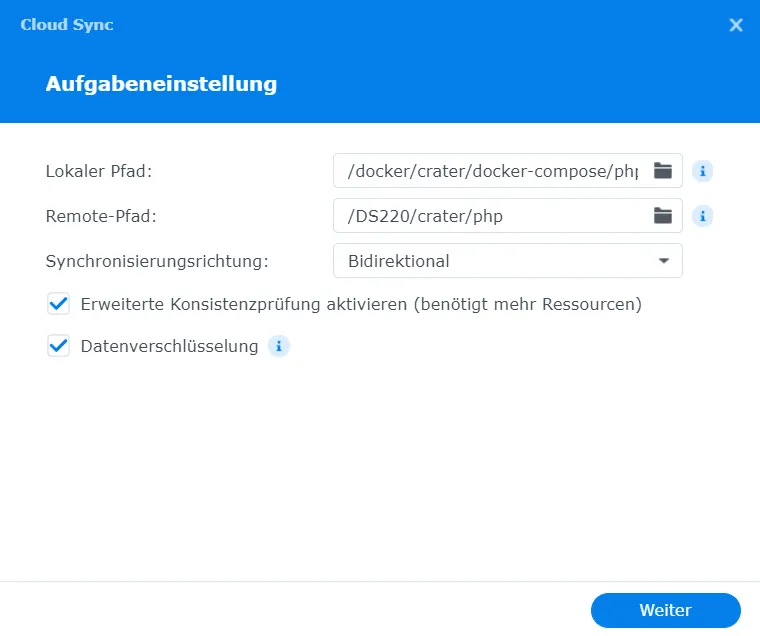
If you want to back up your data in the cloud, this is easy to do on a Synology DiskStation. To do this, install the Cloud Sync program from the Package Center.

With this, I set up a new task that should synchronize the folders docker-compose/db-backup and docker/compose/php with Google Drive or Microsoft One Drive etc.
Please use the comment function for questions / suggestions for improvement / criticism etc.